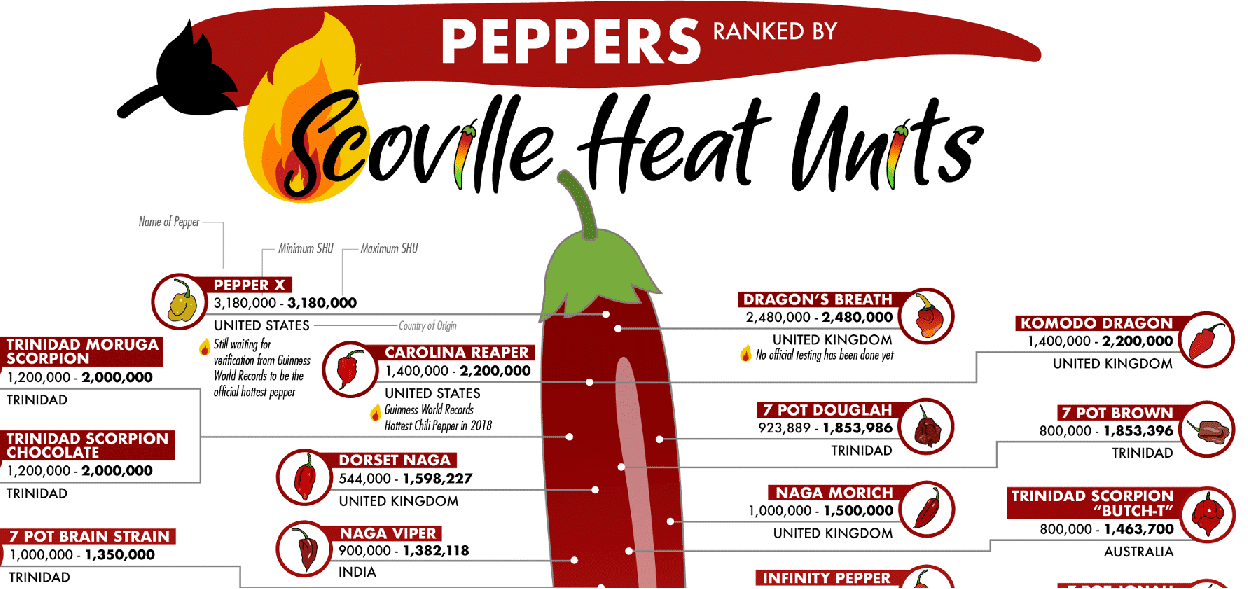
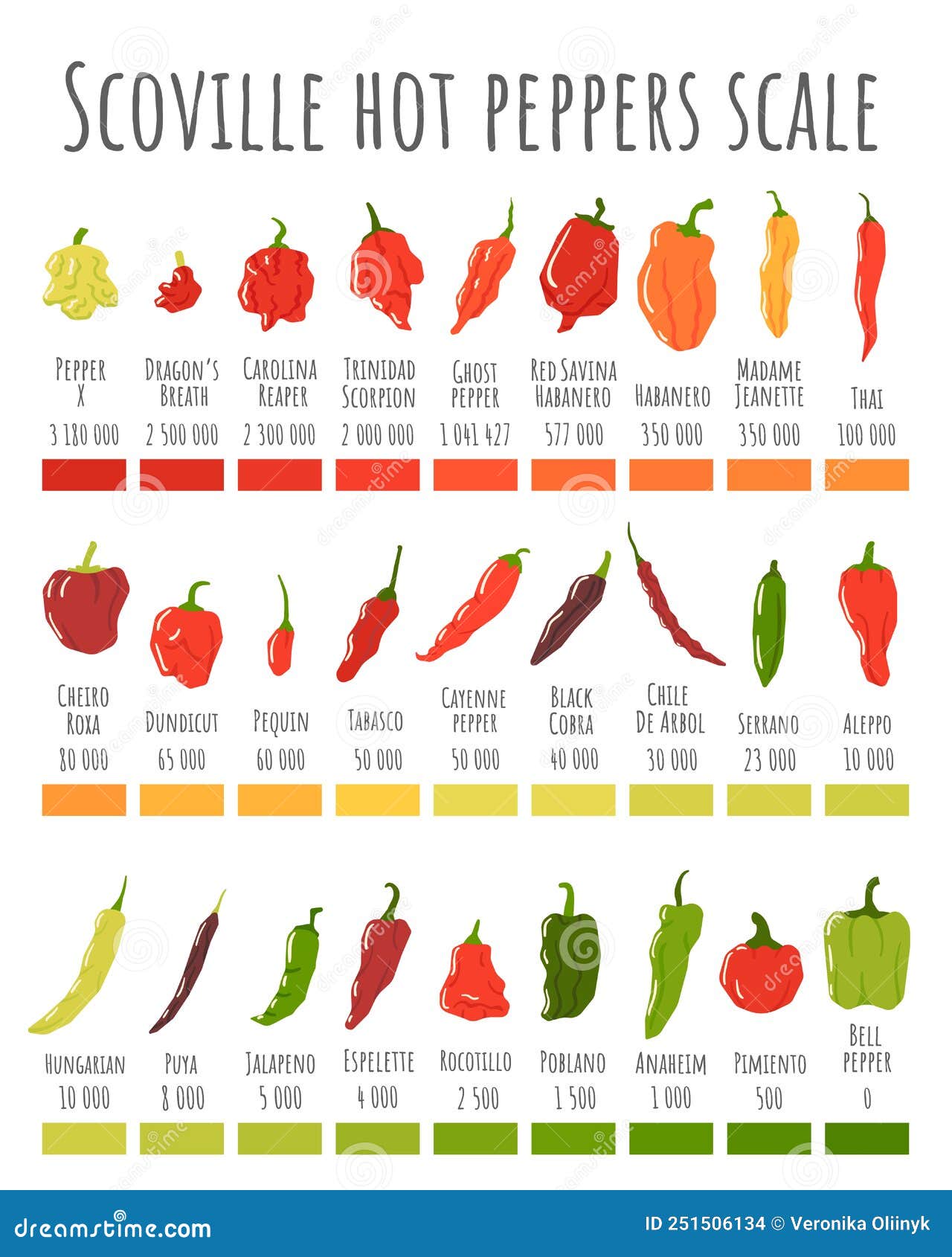
Peppers have been a staple in culinary traditions around the globe for centuries, but few varieties capture the imagination like the hottest peppers by Scoville units. From the fiery heat of the Carolina Reaper to the intense burn of the Trinidad Moruga Scorpion, these chili peppers are not just ingredients—they’re a challenge to the bravest taste buds. If you're a chili enthusiast or simply curious about what makes these peppers so hot, this article dives deep into the world of the hottest chili peppers, exploring their origins, heat levels, and culinary applications.
Understanding the Scoville scale is crucial for anyone interested in hot peppers. The Scoville scale measures the heat of chili peppers in Scoville Heat Units (SHU), giving us a way to compare just how hot each variety truly is. This guide will explore the hottest peppers by Scoville units, offering insights into their origins, characteristics, and culinary uses.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of the hottest chili peppers and their significance in the culinary world. Whether you're a daring foodie or simply fascinated by the science behind chili heat, this guide will provide all the information you need.
Read also:Ronnie Coleman Competition Weight Unveiling The Legendary Physique
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Scoville Units
- Top Hottest Peppers by Scoville Units
- Biological Factors Influencing Pepper Heat
- Cultivation Process of Hot Peppers
- Culinary Uses of Hottest Peppers
- Health Benefits of Consuming Hot Peppers
- Safety Tips for Handling Hot Peppers
- Comparison Chart of Hottest Peppers
- Common Myths About Hot Peppers
- Future Trends in Hot Pepper Cultivation
Introduction to Scoville Units
The Scoville scale is the standard measurement used to determine the heat level of chili peppers. Developed by Wilbur Scoville in 1912, the scale measures the concentration of capsaicin, the compound responsible for the heat in chili peppers. Capsaicin is measured in Scoville Heat Units (SHU), with milder peppers like the bell pepper scoring zero SHU and the hottest peppers reaching millions of SHU.
Understanding the Scoville scale is essential for anyone interested in hot peppers. It provides a clear framework for comparing the heat of different varieties, helping chili enthusiasts make informed decisions about which peppers to try.
How the Scoville Scale Works
The Scoville scale works by diluting a solution of chili extract with sugar water until the heat is no longer detectable by a panel of tasters. The number of dilutions required determines the SHU of the pepper. Modern methods use high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for more accurate measurements.
- Bell Peppers: 0 SHU
- Jalapeño: 2,500–8,000 SHU
- Habanero: 100,000–350,000 SHU
- Carolina Reaper: 1,569,300 SHU
Top Hottest Peppers by Scoville Units
When it comes to the hottest peppers by Scoville units, few varieties can match the intensity of the Carolina Reaper, Trinidad Moruga Scorpion, and Ghost Pepper. These chili peppers are not only hot but also unique in flavor and origin, making them a fascinating subject for chili enthusiasts.
Carolina Reaper
The Carolina Reaper, with an average SHU of 1,569,300, holds the Guinness World Record for the hottest chili pepper. Developed by Ed Currie of the PuckerButt Pepper Company, this pepper is a cross between a Red Habanero and a Naga Viper. Its heat is often described as intense and overwhelming, with a fruity undertone.
Trinidad Moruga Scorpion
The Trinidad Moruga Scorpion, with an SHU range of 1,200,000–2,000,000, is another contender for the title of the hottest pepper. Native to Trinidad, this pepper is known for its sweet, fruity flavor, which contrasts sharply with its intense heat. It’s a favorite among chili enthusiasts for its complexity and heat.
Read also:Santa Clarita Population 2023 An Indepth Analysis And Insights
Ghost Pepper
The Ghost Pepper, or Bhut Jolokia, originated in India and has an SHU range of 855,000–1,041,427. Known for its intense heat and slow-building burn, the Ghost Pepper has become a staple in competitive chili-eating contests.
Biological Factors Influencing Pepper Heat
The heat of chili peppers is influenced by several biological factors, including genetics, growing conditions, and climate. Understanding these factors can help growers produce peppers with consistent heat levels.
Genetics play a significant role in determining the heat of chili peppers. Different varieties have varying levels of capsaicin, which is responsible for the pepper's heat. Environmental factors such as temperature, soil quality, and water availability also impact capsaicin production.
Impact of Growing Conditions
- Temperature: Higher temperatures can increase capsaicin production, leading to hotter peppers.
- Soil Quality: Nutrient-rich soil promotes healthy plant growth and can enhance capsaicin production.
- Water Availability: Stress from lack of water can increase the heat level of peppers.
Cultivation Process of Hot Peppers
Cultivating hot peppers requires careful attention to detail. From seed selection to harvest, every step of the process impacts the final product. Growers must consider factors such as soil preparation, planting techniques, and pest control to ensure healthy plants and consistent heat levels.
Key Steps in Cultivation
- Seed Selection: Choose seeds from reputable suppliers to ensure genetic consistency.
- Soil Preparation: Use well-draining soil with a balanced pH level.
- Planting Techniques: Plant seeds in a sunny location with adequate spacing to promote air circulation.
- Pest Control: Use organic methods to control pests and diseases, ensuring the safety of the peppers.
Culinary Uses of Hottest Peppers
The hottest peppers by Scoville units are not just for daring foodies. They have a variety of culinary uses, from adding heat to sauces and salsas to enhancing the flavor of main dishes. Their unique heat and flavor profiles make them a valuable ingredient in many cuisines.
Popular Culinary Applications
- Sauces and Salsas: Hot peppers are commonly used to add heat to sauces and salsas.
- Spices and Rubs: Ground hot peppers are used in spice blends and rubs for meats.
- Infused Oils: Hot peppers can be infused into oils to add heat and flavor to dishes.
Health Benefits of Consuming Hot Peppers
Consuming hot peppers offers several health benefits. Capsaicin, the compound responsible for the heat, has been shown to boost metabolism, reduce inflammation, and even aid in weight loss. Additionally, hot peppers are rich in vitamins and antioxidants, making them a nutritious addition to any diet.
Key Health Benefits
- Metabolism Boost: Capsaicin can increase metabolic rate, helping with weight management.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: Hot peppers can reduce inflammation in the body.
- Rich in Vitamins: Hot peppers are high in vitamins A and C, supporting immune health.
Safety Tips for Handling Hot Peppers
Handling the hottest peppers by Scoville units requires caution. Capsaicin can cause irritation to the skin and eyes, so it’s important to take proper precautions when preparing these peppers.
Handling Tips
- Wear Gloves: Always wear gloves when handling hot peppers to prevent skin irritation.
- Avoid Contact with Eyes: Wash your hands thoroughly after handling peppers to avoid accidental contact with eyes.
- Ventilate the Area: Ensure proper ventilation when cooking with hot peppers to prevent respiratory irritation.
Comparison Chart of Hottest Peppers
Below is a comparison chart of the hottest peppers by Scoville units, highlighting their SHU range and key characteristics.
| Pepper Name | SHU Range | Origin | Flavor Profile |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carolina Reaper | 1,569,300 SHU | USA | Fruity, Sweet |
| Trinidad Moruga Scorpion | 1,200,000–2,000,000 SHU | Trinidad | Fruity, Sweet |
| Ghost Pepper | 855,000–1,041,427 SHU | India | Earthy, Slow-Building Heat |
Common Myths About Hot Peppers
There are several myths surrounding hot peppers, from their effects on digestion to their ability to cure ailments. Separating fact from fiction is crucial for anyone looking to incorporate hot peppers into their diet.
Debunking Common Myths
- Myth: Hot Peppers Cause Ulcers: Hot peppers do not cause ulcers but can irritate existing conditions.
- Myth: Hot Peppers are Addictive: While capsaicin can trigger endorphin release, it is not addictive in the traditional sense.
Future Trends in Hot Pepper Cultivation
The future of hot pepper cultivation looks promising, with advancements in genetics and technology leading to new varieties with unique heat levels and flavor profiles. As interest in spicy foods continues to grow, so too will the demand for innovative chili pepper varieties.
Innovations in Cultivation
- Genetic Engineering: Scientists are exploring genetic engineering to create peppers with controlled heat levels.
- Sustainable Practices: Growers are adopting sustainable practices to reduce the environmental impact of pepper cultivation.
Kesimpulan
In summary, the hottest peppers by Scoville units offer a fascinating glimpse into the world of chili peppers. From their origins and cultivation to their culinary uses and health benefits, these peppers are a valuable addition to any kitchen. By understanding the Scoville scale and taking proper safety precautions, chili enthusiasts can enjoy the unique heat and flavor of the world's hottest peppers.
We invite you to leave a comment below sharing your favorite hot pepper or any questions you might have. For more exciting content, explore our other articles on culinary trends and spice exploration. Together, let's continue to discover the world of hot peppers and their endless possibilities!