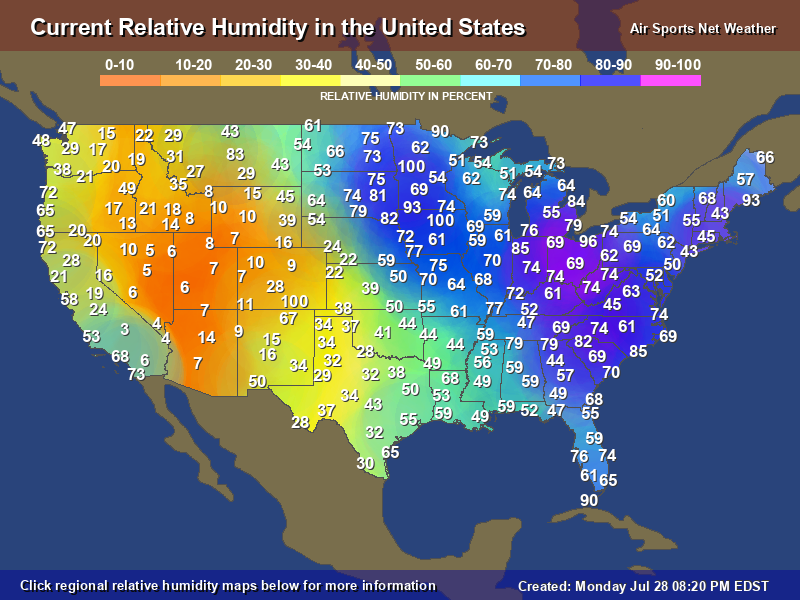
Humidity in the United States plays a crucial role in shaping the climate, influencing daily life, and affecting various industries. Whether you're a weather enthusiast or simply someone curious about the science behind moisture in the air, this article will provide you with a detailed understanding of humidity patterns across the country. From coastal regions to arid deserts, humidity levels vary significantly, creating unique environmental conditions.
Living in or visiting the United States means encountering a wide range of humidity levels depending on the region. This variability can impact everything from comfort levels to agriculture and even health. Understanding humidity is essential for anyone looking to adapt to different climates, plan outdoor activities, or make informed decisions about relocation.
In this article, we will explore the factors that influence humidity in the U.S., regional variations, and the implications of high or low humidity levels. We'll also discuss practical tips for managing humidity in your home and staying comfortable in various climates. By the end of this guide, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of humidity in the United States and how it affects daily life.
Read also:Who Is The Highest Paid Wnba Player Discover The Stars Of Womens Basketball
Table of Contents
- What is Humidity?
- Humidity Patterns in the United States
- Regional Differences in Humidity
- Factors Affecting Humidity Levels
- Effects of Humidity on Health
- Humidity and Agriculture
- Managing Humidity in Your Home
- Seasonal Variations in Humidity
- Impact of Climate Change on Humidity
- Conclusion
What is Humidity?
Humidity refers to the amount of water vapor present in the air. It is typically measured as relative humidity, which expresses the current water vapor content as a percentage of the maximum amount the air can hold at a specific temperature. High humidity levels can make the air feel sticky and uncomfortable, while low humidity can lead to dryness and discomfort.
Types of Humidity
There are several types of humidity, including:
- Absolute Humidity: The total mass of water vapor in a given volume of air.
- Relative Humidity: The ratio of the current water vapor content to the maximum possible water vapor content at a specific temperature.
- Specific Humidity: The ratio of the mass of water vapor to the total mass of air in a given volume.
Understanding these different types of humidity helps meteorologists and scientists analyze weather patterns and predict changes in atmospheric conditions.
Humidity Patterns in the United States
The United States experiences diverse humidity patterns due to its vast size and varied geography. Coastal areas, such as those along the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean, typically have higher humidity levels compared to inland regions. This is because water bodies contribute to increased evaporation, leading to higher moisture content in the air.
Key Influences on Humidity Patterns
Several factors influence humidity patterns across the U.S., including:
- Proximity to Water Bodies: Coastal regions and areas near large lakes tend to have higher humidity levels.
- Elevation: Higher altitudes generally result in lower humidity due to reduced atmospheric pressure.
- Weather Systems: Tropical storms and hurricanes can significantly increase humidity levels in affected areas.
These patterns create distinct microclimates within the country, affecting both natural ecosystems and human activities.
Read also:Dancing With The Stars Voting A Comprehensive Guide To Boost Your Favorite Stars
Regional Differences in Humidity
Humidity levels vary significantly across different regions of the United States. Below is a breakdown of humidity characteristics in major U.S. regions:
1. Northeast
The Northeast experiences moderate to high humidity levels, especially during the summer months. Coastal areas like New England tend to have higher humidity compared to inland regions.
2. Southeast
The Southeast is notorious for its high humidity levels, particularly along the Gulf Coast. This region often experiences oppressive heat and humidity during the summer, making it challenging for residents and visitors alike.
3. Midwest
The Midwest has variable humidity levels, with higher humidity near the Great Lakes and lower humidity in more arid areas like western Nebraska.
4. Southwest
The Southwest is characterized by low humidity levels, especially in desert regions like Arizona and Nevada. However, during the monsoon season, humidity can increase temporarily due to moisture from the Gulf of Mexico.
5. West Coast
The West Coast generally has moderate humidity levels, although coastal areas like California can experience higher humidity during certain times of the year.
Factors Affecting Humidity Levels
Several factors contribute to the variability of humidity levels in the United States:
- Temperature: Warmer air can hold more moisture, leading to higher humidity levels.
- Wind Patterns: Prevailing winds can transport moisture from one region to another, affecting local humidity levels.
- Vegetation: Areas with dense vegetation tend to have higher humidity due to increased evapotranspiration.
- Precipitation: Rainfall and snowmelt contribute to higher humidity levels by adding moisture to the air.
Understanding these factors is essential for predicting and managing humidity-related challenges.
Effects of Humidity on Health
Humidity can have significant effects on human health, both positive and negative:
High Humidity
- Can exacerbate respiratory conditions like asthma.
- Increases the risk of heat-related illnesses, such as heatstroke and dehydration.
- Creates an ideal environment for mold and mildew growth, which can trigger allergies and respiratory issues.
Low Humidity
- Causes dry skin and mucous membranes, leading to discomfort and increased susceptibility to infections.
- Can worsen symptoms of respiratory conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Increases static electricity, which can be a nuisance in certain environments.
Maintaining optimal humidity levels in indoor environments is crucial for promoting health and well-being.
Humidity and Agriculture
Humidity plays a vital role in agriculture, influencing crop growth, pest management, and irrigation needs. High humidity can promote fungal growth and disease in crops, while low humidity can lead to water stress and reduced yields.
Managing Humidity in Agriculture
- Implementing proper irrigation techniques to maintain optimal soil moisture levels.
- Using cover crops to reduce evaporation and maintain soil humidity.
- Employing pest management strategies to combat humidity-related issues like mold and mildew.
By understanding and managing humidity levels, farmers can improve crop health and increase productivity.
Managing Humidity in Your Home
Maintaining comfortable humidity levels in your home is essential for both health and comfort. Here are some practical tips for managing indoor humidity:
- Use a Humidifier or Dehumidifier: These devices can help regulate indoor humidity levels.
- Ventilate Your Home: Proper ventilation helps reduce excess moisture and prevents mold growth.
- Seal Gaps and Cracks: Sealing gaps around windows and doors can prevent moisture from entering your home.
- Monitor Humidity Levels: Use a hygrometer to measure and monitor indoor humidity levels.
Implementing these strategies can create a more comfortable and healthy living environment.
Seasonal Variations in Humidity
Humidity levels in the United States vary significantly throughout the year:
Summer
Summer months generally bring higher humidity levels, especially in the Southeast and along coastal regions. This can make the air feel warmer and more oppressive.
Winter
Winter months often see lower humidity levels, particularly in colder regions. This can lead to dry air indoors, causing discomfort and health issues.
Spring and Fall
Spring and fall typically have moderate humidity levels, providing a comfortable balance between the extremes of summer and winter.
Understanding these seasonal variations can help you prepare for changing conditions and adjust your lifestyle accordingly.
Impact of Climate Change on Humidity
Climate change is expected to alter humidity patterns in the United States, with potential consequences for both natural ecosystems and human societies:
- Increased Evaporation: Warmer temperatures can lead to increased evaporation, resulting in higher humidity levels in some regions.
- More Frequent Extreme Weather Events: Hurricanes and tropical storms may become more intense, bringing higher humidity and flooding risks.
- Shifts in Precipitation Patterns: Changes in precipitation can alter humidity levels, affecting agriculture and water resources.
Addressing the impacts of climate change on humidity requires coordinated efforts to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to changing conditions.
Conclusion
Humidity in the United States is a complex and dynamic phenomenon, influenced by a variety of factors and varying significantly across regions. Understanding humidity patterns, their effects on health and agriculture, and strategies for managing indoor humidity can help individuals and communities adapt to changing conditions.
We encourage you to explore further resources and stay informed about humidity-related developments. Feel free to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below, and consider exploring other articles on our site for more insights into climate and weather topics.
References:
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
- World Health Organization (WHO)