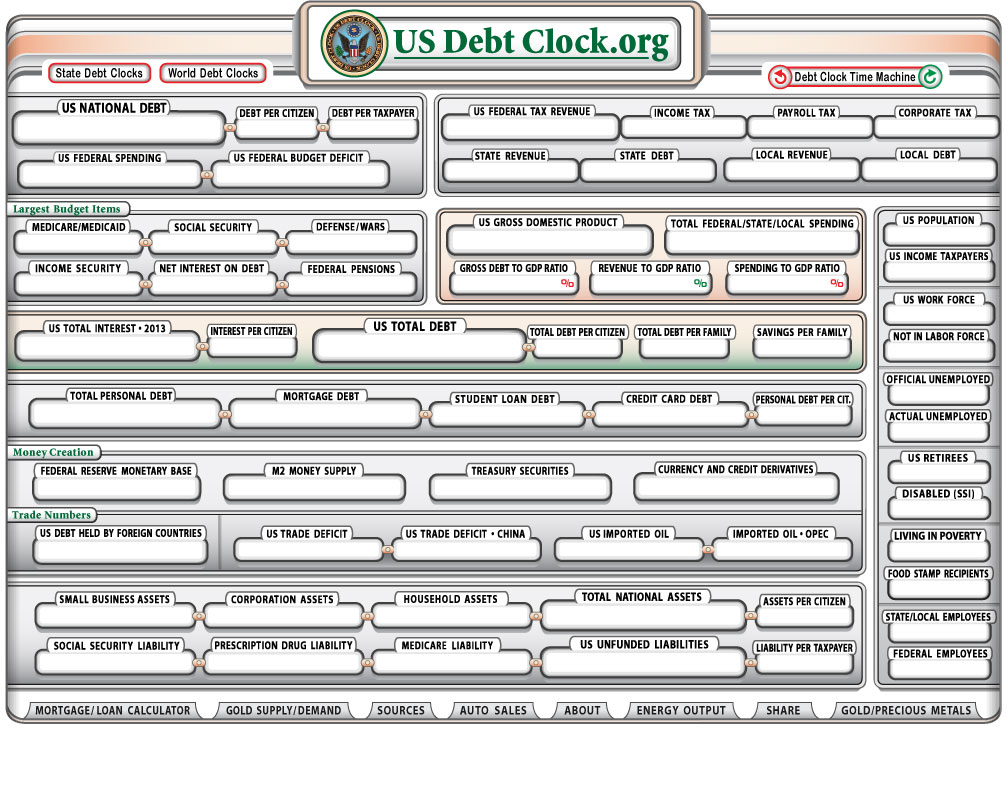
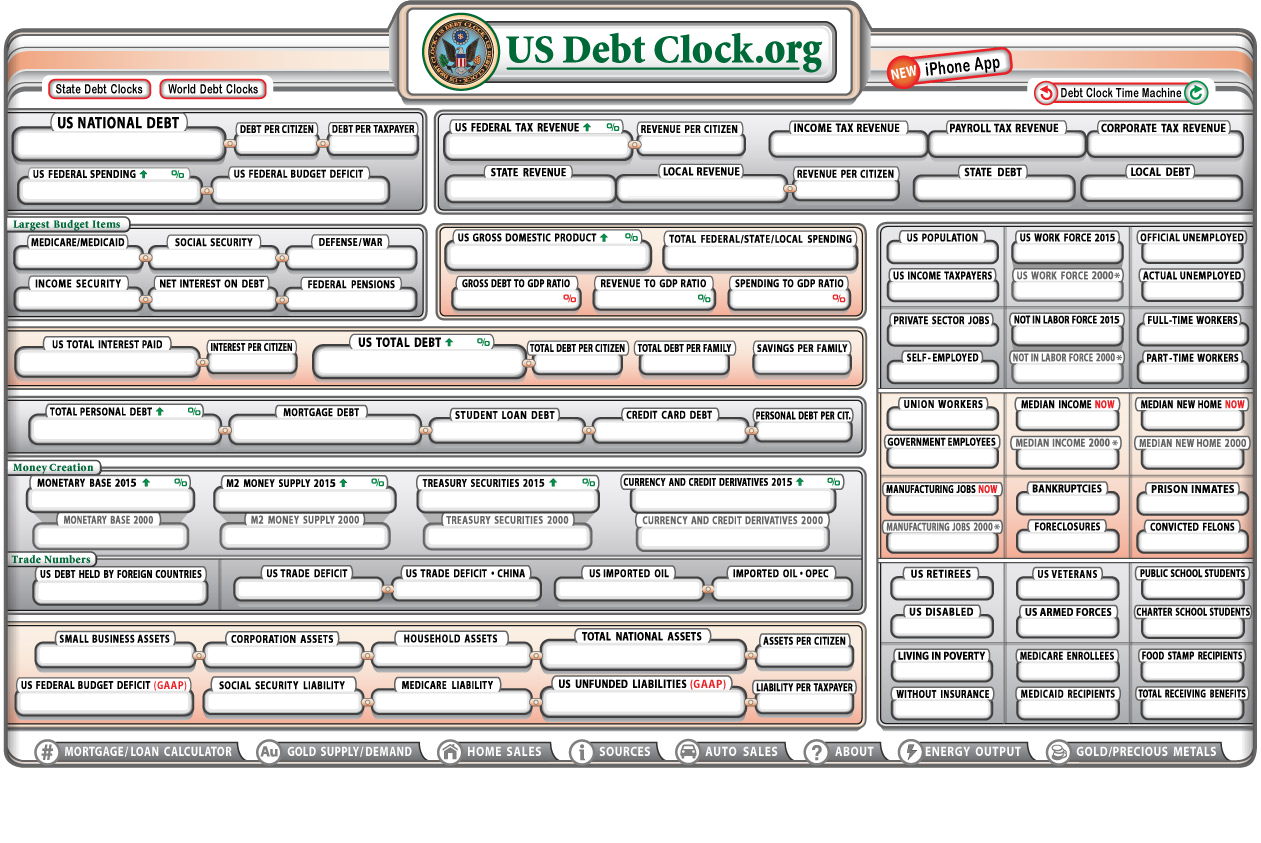
The United States Debt Clock real time is a critical tool that provides insight into the financial health of the nation. It tracks the growing national debt, which has become a significant concern for economists, policymakers, and citizens alike. As the U.S. debt continues to rise, understanding its implications becomes essential for everyone.
With the national debt surpassing $31 trillion as of 2023, it is crucial to examine the factors contributing to this figure and the potential consequences for the economy. This article aims to break down the complexities of the U.S. debt clock and explain why it matters to individuals and businesses.
By exploring the history, causes, and effects of the national debt, we can gain a clearer picture of the economic landscape. Whether you're a student, investor, or concerned citizen, this guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about the future of the U.S. economy.
Read also:Who Is The Highest Paid Wnba Player Discover The Stars Of Womens Basketball
Table of Contents
- What is the United States Debt Clock?
- History of the U.S. National Debt
- Factors Contributing to the National Debt
- Effects of the National Debt on the Economy
- Real-Time Tracking of the U.S. Debt
- Government Responses to the Debt Crisis
- Impact on Taxpayers and Future Generations
- Comparison with Other Countries' Debt Levels
- Ways to Reduce the National Debt
- Conclusion and Call to Action
What is the United States Debt Clock?
The United States Debt Clock real time is a digital display that tracks the national debt of the United States. It provides up-to-the-second updates on the total amount of money the federal government owes to creditors, both domestic and foreign. This clock serves as a visual reminder of the growing financial obligations of the nation.
The debt clock was first introduced in 1989 by New York real estate developer Seymour Durst. Since then, it has become an iconic symbol of the nation's fiscal challenges. The clock is now available online, allowing anyone to monitor the debt in real time.
How Does the Debt Clock Work?
The debt clock calculates the national debt by tracking the issuance of government securities, such as Treasury bonds, bills, and notes. It also considers factors like federal budget deficits and interest payments on existing debt. The clock updates automatically as new data becomes available from government sources.
Key statistics displayed on the debt clock include:
- Total national debt
- Per capita debt
- Debt-to-GDP ratio
- Interest payments on the debt
History of the U.S. National Debt
The U.S. national debt has a long and complex history, dating back to the country's founding. The first significant increase in debt occurred during the Revolutionary War, when the government borrowed money to finance its fight for independence. Since then, major wars, economic recessions, and government spending programs have contributed to the growth of the debt.
Key Historical Milestones
- World War II: The debt surged to fund military efforts, reaching over 100% of GDP.
- 1980s: Tax cuts and increased defense spending under President Reagan led to higher deficits.
- 2008 Financial Crisis: Bailouts and stimulus packages added trillions to the debt.
- COVID-19 Pandemic: Relief packages and economic recovery efforts caused a sharp increase in debt.
Factors Contributing to the National Debt
Several factors have contributed to the rise of the U.S. national debt over the years. Understanding these factors is essential for addressing the issue effectively.
Read also:Carl Grimes The Legacy Of A Beloved Character From The Walking Dead
1. Government Spending
Increased government spending on programs like Social Security, Medicare, and defense has added significantly to the debt. Mandatory spending programs account for a large portion of the budget.
2. Tax Revenues
Insufficient tax revenues, often due to tax cuts or economic downturns, have widened the gap between spending and income, leading to larger deficits.
3. Interest Payments
As the debt grows, so do the interest payments required to service it. These payments further strain the federal budget.
Effects of the National Debt on the Economy
The national debt can have both short-term and long-term effects on the economy. While moderate levels of debt can stimulate growth during recessions, excessive debt can lead to negative consequences.
Short-Term Effects
- Increased borrowing costs for businesses and consumers
- Potential inflationary pressures
- Reduced flexibility in fiscal policy
Long-Term Effects
- Slower economic growth
- Higher interest rates
- Decreased investment in critical areas like infrastructure and education
Real-Time Tracking of the U.S. Debt
Tracking the U.S. debt in real time is crucial for staying informed about the nation's financial health. Several websites and tools provide up-to-date information on the debt clock, including:
These platforms offer detailed breakdowns of the debt, including per capita figures and debt-to-GDP ratios.
Government Responses to the Debt Crisis
Over the years, the U.S. government has implemented various measures to address the national debt. These include budget reforms, spending cuts, and revenue-enhancing policies.
Recent Efforts
- Budget Control Act of 2011
- Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018
- American Rescue Plan Act of 2021
Despite these efforts, the debt continues to grow, highlighting the need for sustained and comprehensive solutions.
Impact on Taxpayers and Future Generations
The national debt has direct implications for taxpayers and future generations. Higher debt levels mean increased interest payments, which can crowd out spending on essential services like education and healthcare.
Key Concerns
- Higher taxes to fund debt payments
- Reduced government services
- Intergenerational inequality
Addressing these concerns requires proactive measures to ensure the financial well-being of future generations.
Comparison with Other Countries' Debt Levels
The U.S. national debt is among the highest in the world when measured in absolute terms. However, when compared as a percentage of GDP, other countries like Japan and Greece have even higher debt levels.
Global Debt Trends
- Japan: Over 250% of GDP
- Greece: Around 200% of GDP
- United States: Approximately 120% of GDP
These comparisons highlight the importance of managing debt responsibly to avoid economic instability.
Ways to Reduce the National Debt
Reducing the national debt requires a combination of strategies, including:
1. Fiscal Responsibility
Implementing responsible fiscal policies that balance spending and revenue.
2. Economic Growth
Promoting economic growth to increase tax revenues and reduce the debt-to-GDP ratio.
3. Budget Reforms
Reforming entitlement programs and reducing unnecessary spending.
By adopting these approaches, the U.S. can work toward a more sustainable fiscal future.
Conclusion and Call to Action
The United States Debt Clock real time serves as a powerful reminder of the nation's financial challenges. By understanding the causes and effects of the national debt, we can take steps to address this issue and ensure a stable economic future.
We encourage readers to:
- Stay informed about the debt clock and its implications
- Engage in discussions about fiscal policy with policymakers
- Explore additional resources on our website for more insights
Together, we can make a difference in shaping the financial future of the United States.
For more information, please refer to the following sources: